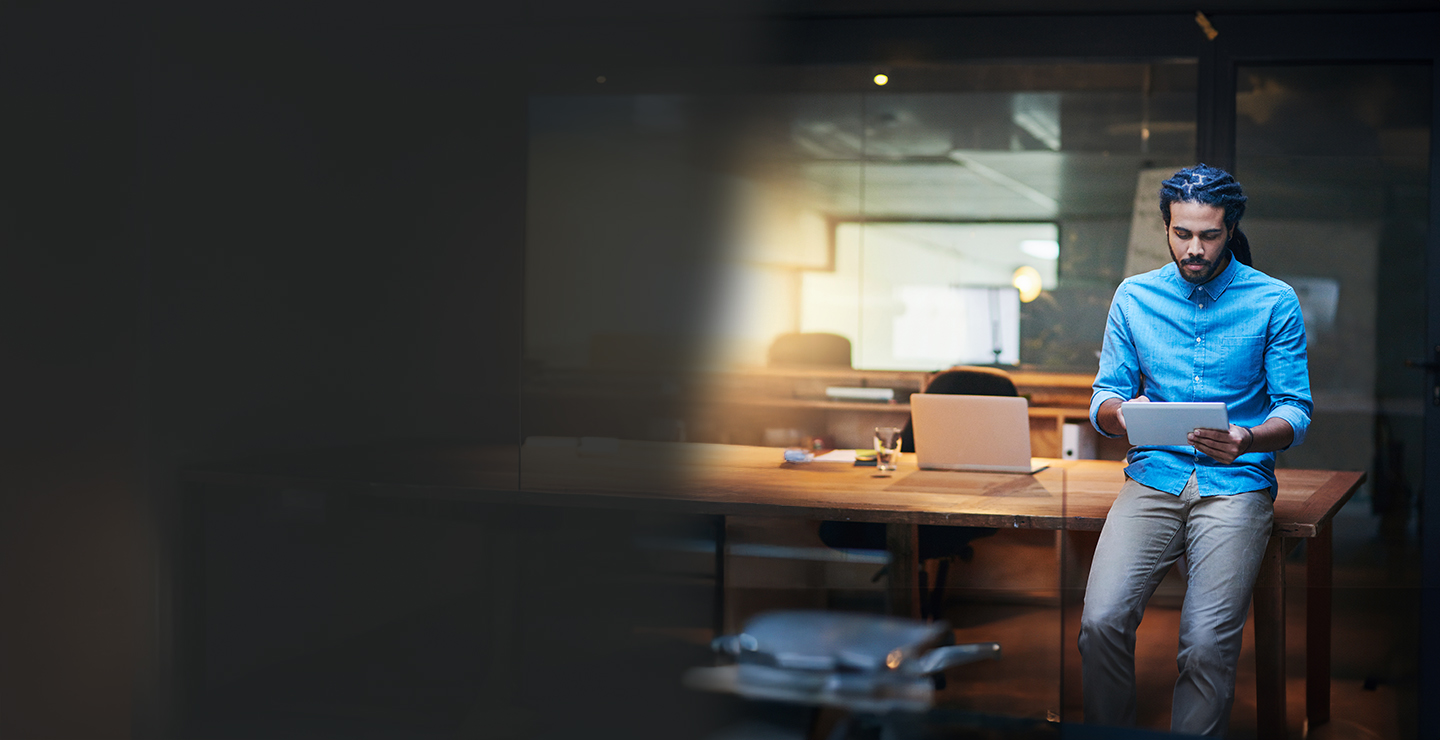
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the insurance industry, presenting both significant opportunities and complex governance challenges. As AI becomes embedded across operations, carriers must adopt robust governance frameworks, rigorous data management, and comprehensive risk mitigation strategies. This briefing distills industry best practices to guide organizations in managing and mitigating AI risks throughout the project lifecycle - whether developing systems internally or procuring from third-party vendors.
It is strongly recommended that executives ensure that:
- There is clear alignment of AI initiatives with business objectives and regulatory expectations.
- Your firm is conducting and institutionalizing transparent vendor vetting and data testing.
- You have implemented proactive governance and compliance measures.
- Are promoting enterprise-wide AI literacy and cross-functional ownership.